Cartesian Coordinate System:
Cylindrical Coordinate System:
Spherical Coordinate System:
==========================================================
Similarity Between Triangles:Similarity Between Triangles Example:
=========================================================
Absolute Value Inequalities:
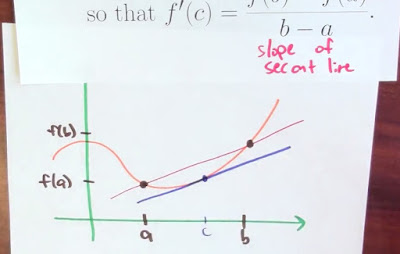
===========================================================
Numbers:
Conics:
Coefficients:
The primary function of the Coefficients method is to allow you to create any conic (circle, ellipse, parabola, or hyperbola), given the equation of the conic.
You enter the coefficient values of the mathematical equation as A through F in the parameters dialog. The values control the size, type, and orientation angle of the conic (based on the location of the WCS). NX uses a general equation for all conic types as long as A, B, and C are not all zeros.
A quick way to determine what the result will be is to use the A, B, and C values in the following two formulas.
- If A=C and B=0 The result is a circle.
- For B2 - 4AC=X If the result is greater than 0 a hyperbola is created.
- If the result is equal to 0, a parabola is created.
- If the result is less than 0, an ellipse is created.
Ellipse:
Hyperbola:
Curvature of a Curve:
Trigonometry in Motion:
Fourier Series in Motion:
Degree-Radian Conversion:
Sine Function:
Sine & Cosine Conversion:
Phase Angle:Sine & Cosine Phase Angle:
Phase Shift in Sine Function Example:
Phase Shift Example:
==========================================================
Angular Velocity - Linear Velocity Conversion:
=========================================================
Polynomial: In mathematics, a polynomial is an expression consisting of variables (also called indeterminates) and coefficients, that involves only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and non-negative integer exponentiation of variables. An example of a polynomial of a single indeterminate x is x^2 − 4x + 7. An example in three variables is x3 + 2xyz2 − yz + 1
A linear polynomial is any polynomial defined by an equation of the form. p(x) = ax + b. where a and b are real numbers.
=========================================================
Euler's Method (Approximation):
Example 1:
Example 2:
Example 3:
Graphs of Trigonometric Functions:
Example 1:
Example 2:
Example 3:
Example 4:
Example 5:
===========================================================
=========================================================
=====================================================
=======================================================
Wolfram Alpha - Tutorial 1:
Wolfram Alpha - Tutorial 2:
=======================================================